Industrial Strength IT Projects Deliveries
Current Industry and Government Funded Research Projects

Industry funded project flow out of ARC LP and CRCP
Project Sponsor: Fleetwood Australia Limited, Glyde Digital PL, ISS and Defence E&IG, KSR
Project Leaders: Mr. Steve Wallis (CTO Fleetwood), Prof. Elizabeth Chang (UNSW), Dr. Ponnie Clark (UWA)
The Project address 3 key problem for workforce accommodations, including:
- Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) and Covid-19 pandemic Resilience, contactless, contact tracing, social distancing, within the domestics and remote environments, sites and facilities. The project concerns about wellbeing of occupants, business compliance, assurance and risk management.
- Optimise resources and energy consumptions for OHS, ensure low cost and sustainable solutions.
- Security and Privacy for , currently use contact-based entries, such as swap cards, or figure print, or pen and pencil down the logbook. Require admin officer, costly and not secure in terms of Covid-19 pandemic.
The project is to address key challenges in dealing with massive influx of occupants in site, camps, Office buildings, FIFO workers. In the pandemic situation, the contactless technology is critical technology for resilience, better environment, and improved social, health and safety conditions.

Digital Transformation of Commercial Fleet Management for E&IG, Defence
Project Sponsor: Department of Defence
Project ID: RG204500
Project Leaders: Dr. F. Gottwalt, Mr. S. Green, Prof E. Chang
This project is to through collaborative effort and co-innovation to improve customer service and customer experience between E&IG that uses AI to reduce administrative burden, manual-based operations and improve the customer experience for DLOG-EIG. It develops an advanced artificial intelligent solution and Blockchains platform for management of vehicle life cycles, performance, availability and maintenance for Defence users.
CASG Innovation Competition – AI and Blockchain enabled National Vehicle Compliance Auditing
Project Sponsor: Department of Defence
Project ID: RG201418
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Dr. F. Gottwalt, Mr. S. Green
The project uses AI and machine learning of big data to manage vehicle operation risks as part of Compliance Assurance Risk Management framework. The key component is to develop advanced algorithms to adequately interprets heterogenous data sources, data types and data semantics, this includes all type of documents, photographs, web forms, handwriting forms and signatures etc. The project use AI to identify the anomaly and refer back to the operators to rectify all risk activity and we predict vehicle maintainability, availability and serviceability.

Automated Inventory Pricing Assurance Auditing
Project Sponsor: Department of Defence
Project ID: RG191288; RG192198
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Dr. F. Gottwalt, Mr. S. Green
This project develops an Automated Artificial Intelligent Diagnostic Tool for Procurement in Material Logistics. In working with Australian National Audit Office (ANAO) and utilises the National Asset Inventory Sampling to assess the Department of Defence’s capability to manage its asset. (Approx 75 Billion Dollars’ worth). This project produced a tool for the Dept of Defence and help Defence to fulfill its obligation on its accuracy in financial statements for the transactions conducted in the past 12 months and support sampling and auditing processing.
Digital Government Transformation in Asset Management and Field Trial
Project Sponsor: Department of Defence
Project ID: RG192198
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Dr. F. Gottwalt, Mr. S. Green
The project produced an Artificial Intelligent Diagnostic tool that can automatically identify different internal and external purchase orders, highlight the procurement process utilised and construct a report pinpointing the transaction and the appropriate method. Utilising the procurement routing rules, the tool would intelligently state which process should have been undertaken and highlight all of the extra work and governance that has been undertaken or required as a result of the incorrect procedure, and field trial the tools with many SPO officers in NSW, Victoria and WA.

Digital Government, Compliance Assurance Risk Management
Project Sponsor: Department of Defence
Project ID: RG201308
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Dr. F. Gottwalt, Mr. S. Green
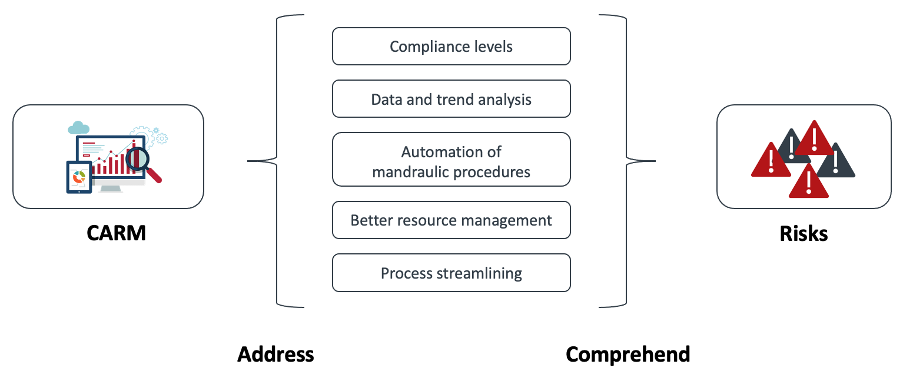
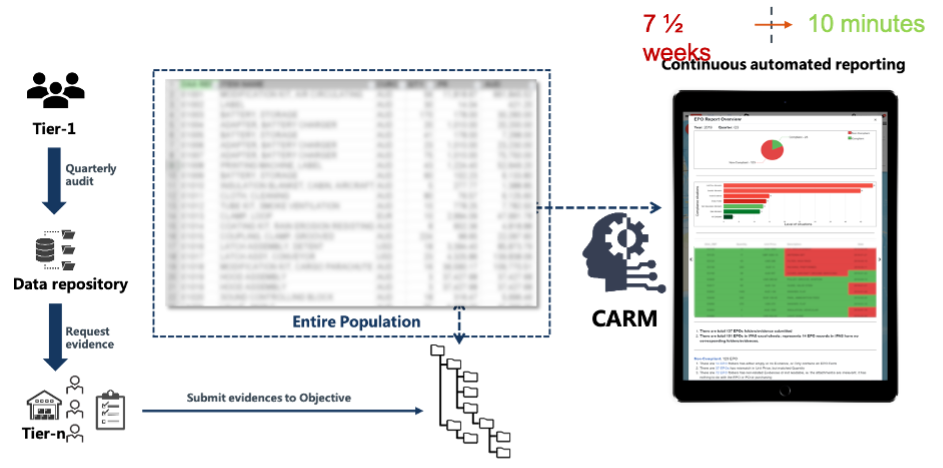
This project invents a Blockchain enabled Compliance Assurance Risk Management Tool (CARM), that can track and trace accountability, user behaviours, roles, and responsibilities. It uses the Blockchain as a Data-Lake to aggregate multi-, heterogeneous data sources and provides immutable, open, and secure Single Source of Truth. It is coupled with data security, trust, privacy, data traceability, aimed at potential saving billions of dollars on enterprise data management. CASG has identified 40+ risks, and we apply this system to the first critical risk, known as stock discrepancies. The project applied the Blockchain and AI for automated mobility enabled stocktakes, risks in non-compliance, and root cause analysis for discrepancies, and 10 field tests at LEAW and ARMT SPO in Victoria, presented $1.2M saving per year on the stocktake activity alone. The project also developed eight other applications in the field of stock takes, including HOTO (Handover, Take Over), Spot Checks, Contractor’s Stocks Takes as first found to MILIS etc.

Digital Government - Light Rail Asset Mapping and Heterogenous Data Integration and Management
Project Sponsor: ACT Transport
Project ID: RG204459
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Dr. M Ghasribouzani, Dr Z. Saberi, Ms. K. Kameliya, Dr. Y Zhang
This project will innovate on Big Asset Data Management strategies for Transport Canberra and City Services (TCCS). The project starts with an Internship program with two recent PhD graduates from UNSW@ADFA. The project aimed to develop a solid proposal on (1) addressing the issues with the Data access from the vendor managed systems, provide finding, analytics and reporting; and (2) to proposal Data migration strategies from legacy systems and vendor managed systems to a new corporate system purchased by TCCS.

Machine Learning and Contextual State Reasoning to Reduce False Positives in Anomaly Detection
Project Sponsor: CRC-Cyber Security
Project ID: RG201418
Project Leaders: Mr. M Zipperle, Prof E. Chang, Dr. F. Gottwalt, Prof TS Dillon, Prof M. Whitty
The proposed research aims to develop contextual features analytics and semantic reasoning to false alarm detection and removal and to address the key issues facing cybersecurity. These include 1) big streaming data analysis, 2) the huge number of generated alarms with the vast majority being false alarms, 3) mandraulic human effort to investigate alarms to find intrusions, and 4) determination and removal of false alarms.
Machine Learning-based Multiple Object Recognition and Classification
Project Sponsor: Department of Defence
Project ID: RG192198
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Dr. F. Gottwalt, Mr. M. Zipperle, Dr. Y. Zhang
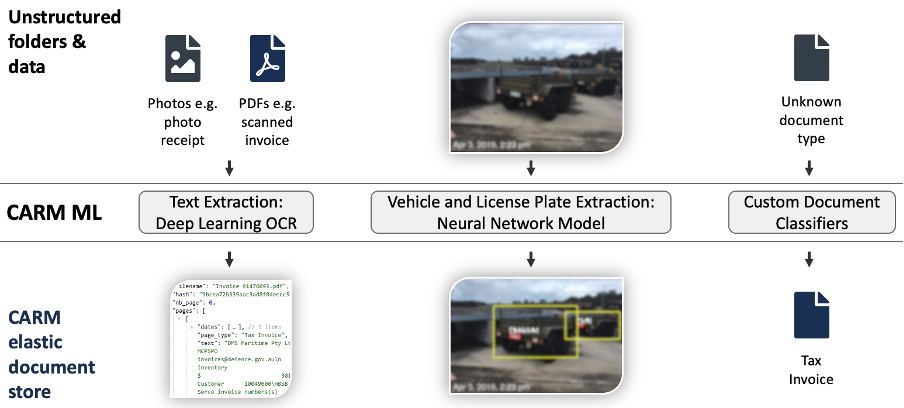
The process from unstructured data to structured data involves the discipline of multiple machine learning approaches such as deep learning or linear regression. Our research group is in a unique position in conducting highly-efficient machine learning research for industry practice through access of large real-world data sets.
A Blockchain-based Compromise Tolerant Private Key Management for Consensus Nodes in Enterprise Data Security
Project Sponsor: CRC-Cyber Security
Project ID: RG204331
Project Leaders: Mr. M Becherer, T Bui-Nguyen, Dr. K Joiner, Prof E. Chang
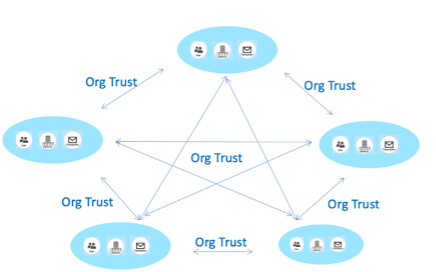
The project seeks to provide enterprise data security, such as financial institution or military operations, by developing a Private Blockchain. The key challenge for private blockchains is the compromise of the trusted Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). While the invention of PKI has solved several security issues in inter- and intra-organisational communication, the security method used to manage those keys is still reliant on centralised management. Such an architecture introduces a number of risks including a) trust reliance on a few system administrators creating an insider threat, b) potential compromise of transactions, identities and organisation reputations, c) single-point-of-failure, and d) defeat of the distributed trust introduced by the invention of public blockchains. To mitigate these risks, this research proposes a compromise-tolerant key management approach that combines decentralised blockchain-based key management with the enforcement of multi-signature. Powered by smart contracts, processing transparency along the certificate lifecycle is enabled among all network participants to establish trust and to mitigate insider and outsider threats.

Intelligent CRM through Conjoint Data Mining of Heterogeneous Sources
Project Sponsor: ARC LP projects and Industry funds 2014-2021
Project ID: RG142563; RG152641; RG152642
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Prof TS Dillon, Prof W. Rahayu, A.Prof O Hussain, Dr. R. Soley, Dr Morteza Saberi
This project provides real-time data quality, accuracy, and transparency methods and techniques for government and private sectors. It integrates data, information and knowledge from heterogeneous business information resources aimed at providing competitive world class customer service and retention. It develops techniques for improving customer relationship management (CRM) for public and private organizations. It manages multiple information resources for information sharing, synthesizes knowledge through visualization and business intelligence. The project produced standardized XML profiles for the different data sets and business processes, novel techniques for conjoint mining of structured and semi-structured data and adaptive business intelligence techniques and the results is validated using large real-world data sets provided by the partner organization.

Green Logistics through Cyber Physical Systems
Project ID: RG152660; RG162763, RG162764
Project Leaders: Prof E. Chang, Prof TS Dillon, A. Prof O Hussain, Dr Atafe Zekeri
This project focus on increasing the industry’s future productivity by looking at alternative sources of fuel that produce economies of operation. Statistics show that an increase in logistics productivity of 1% will increase Australia’s GDP by $2 billion. This project aimed at creating values to industry & the Commonwealth by providing vital data on sustainability issues. Transportation systems account for 18% of Australia’s carbon emissions and diesel-powered logistics vehicles are a major contributor. We develop techniques in this evidence-based project by utilizing actual field data collected in situ. to convince logistics companies of the benefits of shifting to green logistics.

A Knowledge Translation Portal for Australian Veterans Wall of Remembrance
Project Leaders: Mr. Tamara Green, Dr. Keith Joiner, A/Prof O. Hussain, Prof M. Whitty
This project will develop Australian Veterans Wall of Remembrance Knowledge Translation Portal for suicide prevention of the veteran community, aimed to establish greater due-diligence, shared-responsibility, and joint-accountability to suicide prevention. It does that by obtaining the voices and opinions from non-government, not-for-profit organisations, and self-organised veteran social communities such as, Soldier On Australia, Contact Magazine, Veterans for Peace, and self-organised veteran Remembrance Facebook groups. These groups include current and former serving members, veterans and veterans’ families (including spouse, children and parents).
Example of the voices and opinions include debate on the government’s definition of “veteran suicide” versus how it is defined by the veteran community; the voices and opinions regard government published suicide data and data from the veteran communities; and the voices and opinions regard what the government’s suicide prevention programs “should be”, to the solution “could be” from veteran communities.
Completed Industry Based Research Projects
Logistics systems in today’s world are characterized by increasing dynamicity which arises from the trends of global economy. Defence & Business are no exception to this trend & require high quality decision-making support systems to optimize their logistics operations & meet the challenges. Big Data provides a wealth of information from which data can be analysed real time and knowledge synthesized from it. However, before this can be achieved appropriate tools & techniques are needed first to understand the semantics of Big Data, integrate Big Data & apply predictive analytics on it[JMC1] . In this project, we develop the foundation blocks to achieve this aim.
Defence logistics underpin Defence capability. An essential component of successful logistics systems is interoperability – the capacity for diverse systems to work together. However, diverse and separately developed information systems currently comprise the Defence logistics approach. Army operates the Military Integrated Logistics Information System (MILIS). However, the stove-pipe nature of MILIS resulted in interoperability issues with other systems in defence such as SLIM (Ships Logistics Inventory Management System) and Air Log (Air force logistics systems). All three systems are independently auditable. However, there are no synchronised support functions to allow unified inventory and asset tracking. This project seeks to address this issue.
Data mining as a core capability is an intrinsic part of every intelligent organization and enterprise since 9-11 terrorist attacks in the USA in 2001. It is used not only for counter terrorism cyber security, fraud detection, but also as a core technology is used in domains, including commerce and science, such as business intelligence; human disease studies, energy, global warming and social networks[JMC2]. One of the core objectives of data mining is to discover new and useful patterns from data that gives rise to discovery of new and previously unknown information and knowledge. In this project we develop Data Mining techniques to achieve the Intelligence in Defence applications
Defence assets comprise approximately $40.3 billion of specialist military equipment, $21.1 billion of land building and infrastructure and $5.7 billion of inventory. These significant financial expenditures, along with some of the recent incidents that demonstrate poor Risk management in Asset sustainment practices, brings with it questions regarding Australian Army’s effectiveness in establishing, implementing, and improving risk management practice in its assets sustainment in land force operational support. Best practices on Asset Management and ISO standards in recent years have provided with a Total Life Cycle Asset Management (TLAM), which stresses on a clear definition of risk measurement dimensions and risk prediction techniques in the context of Asset management. The objective of this research project is to develop such a cognitive tool that will eventually lead the Army in better risk management of their assets in the future.
The Navy Ships as Warehouses in MILIS project was started in 2012 through contractors like Deloitte, KPMG and CSC Australia. It is intended to enhance Navy’s existing Logistics Warehouse System. However, it has not moved beyond the definition stage. This project is to review existing legacy systems, data misalignment, account structure and to develop new proposals and techniques for enhancements to data alignment, systems interfaces and improve the systems dependencies in ADF Logistics Information Systems environment. In addition, address the organisational change issues such as Ships crew workload, training and business process change is also required.
In this project, our objective is to investigate and identify the root causes for the non-achievement of the SWIM objectives. The significance of the project is that it does not consider the problem as an Information Technology related one but looks it as a conjoint one that arises from people, processes, personnel and systems. Taking those factors into consideration, we will develop a report that that comprises of our analysis and recommendations.
The aim of this project is to develop a Risk Assessment as a Service (RaS) module that enables the service users of Cloud Computing services to make informed service-based decisions with the service providers. Developing such a framework will address one of the major obstacles of Cloud Computing mentioned in the literature. A prototype system of the proposed framework will be developed in this project that can be applied and tested in situ
Large amounts of data is collected and stored by various, government, industrial, commercial or scientific organisations and consists of (1) structured data, eg Asset Databases and (2) semi-structured/unstructured content such as customer complaints. As the complexity and volume of the data continue to increase, the task of classifying new unseen data and extracting useful knowledge from the data is becoming practically impossible for humans to do. This project develops a methodology for performing advanced analytics from both data and content conjointly. The techniques developed will be used to address important issues in Defence enterprise, business organizations and health medicine domain
This project investigates and develops techniques for Intelligent Asset Management. It mines and tracks multiple information resources for accurate Asset information sharing, knowledge synthesis and financial accountability through the use of Ontologies and XML profiles. Novel techniques for conjoint mining of structured and semi-structured data and management will be developed. The results will be validated using large real-world data sets provided by the partners
MIMOS (called MiMorph) has been successfully applied to the merging and cleansing of large real databases for PERKASO/SOCSO (Social Security department of Malaysia). There are a number of research issues which must be addressed for the development of the next generation of Data Merging and Data Cleansing Techniques and Tools. This project is designed to address these issues to allow MIMOS to be at the cutting edge of this highly significant Technology and move MIMOS into a world leading position in Data Merging and Data Cleansing.
In this project, the aim is to develop such an advanced Cyber Physical Systems for Intelligent Asset Tracking in Defence Logistics. Specifically it will develop a Cyber Physical Systems with enhanced Internet of Things, Auto ID Systems, Digital Pens and Smartphone Technologies for Intelligent Asset Tracking and Provenance of Goods and Assets for the future Australian Defence Force. It will result in considerable efficiency, productivity, capability development and lead to benefits for the Australian Defence and the commercial logistics sector as well.
In this research, we intend to develop such a framework on identifying, determining, assessing, mitigating and monitoring the source of risks, with the following 5 major steps:
- identifying the risk sources in the logistics network;
- determining the probability of failure or probability of the occurrences of those risks that may lead to failure in the logistics network;
- ascertaining the adverse consequences in the logistics network as an occurrence of those risks;
- assessing the impact of losses on financial, human and resources; 16 Centre of Excellence for Logistics Innovation and Information Dominance Research 2019 – 2020 Centre of Excellence for Logistics Innovation and Information Dominance Research 2019 – 2020 17
This thesis will address the issue by defining
- type of subtrees to be mined (embedded, induced or ordered)
- support definitions or constraints (transaction based support, occurrence- match support or hybrid-support) depending upon the aims of the query and the way how the information is organized in the augmented database.
- The association rules that are to be synthesized, extracted knowledge pattern should be analysed for their interestingness and relevance to remove any redundant, misleading and irrelevant rules. The aim is to increase the confidence in the determined association rules being a true reflection of the patterns that exist in the underlying augmented data.
Current research into purchase decisions in business markets suggest that commitment and switching costs are the primary reasons for customer loyalty. This study suggests that a third category also exists. “Relational inertia” occurs when repeat purchases from one supplier are due to habit or conservatism. This study considers two perspectives. At the individual level, purchase decisions are one of many demands that individuals face. Drawing on bounded rationality theory and job demands theory, it is likely that individuals consent to repeat purchases due to excess cognitive load. At the firm level, relational inertia may result from cultural conservatism, decision avoidance from senior managers and the presence of specific firm processes that align to the supplier. The overall objective of this study is to uncover the degree to which i) relational inertia is present in different purchase contexts (e.g. industry, product type, firm size, location) and, ii) to determine its relative effects on firm purchase decisions.
Most firms use ‘buying centres’ – groups of representative individuals – to make purchase decisions on behalf of the firm. These individuals exercise purchase authority on behalf of the firm as a whole and so this raises an important agency problem: do they serve all stakeholders’ interests equally well? This study seeks to investigate the degree of stakeholder perceived justice present in buying centre decisions. Three perspectives are of interest in this study. First, the formation of the buying centre shapes decisions, particularly in terms of membership stability, the definition of responsibility scope, and the parameters of the decision-making process. Second, the nature of the product/ service may influence the buying centre decision process; more complex products are likely to require greater expertise; services are likely to be more subjective. Third, user evaluations are likely to focus on engagement with products and services over time. These usage experiences are separate from the purchase process.
The conflict between economic (the profit motive) and customer needs is a well-documented phenomenon facing firms. However, few studies consider the nature of this trade-off across supply chain networks, particularly in life or death customer circumstances. This study seeks to understand this trade off across three primary dimensions. First, the nature of supply chain networks is such that the responsibility for fulfilling customer needs is distributed amongst supply chain network members. How does this distributed mode of responsibility influence end user outcomes? Second, most supply chain network members divide their focus between working collaboratively with other supply chain network members and on internal issues. To what extent does customer orientation exist in specific actors within the supply chain? How does this affect the economic-social trade-off? Third, what approaches or methods (i.e. resources, systems, capital) have supply chain members used to adapt to these circumstances? We have taken conscientious efforts to develop its core competencies in several key areas through internally funded projects. Projects such as data mining, data cleansing, business intelligence and SMEs, corporate social responsibility, assistive devices, smart homes, smart grids, ontologies, cloud computing, service oriented architectures, spam filters, social networks, regional education and skill shortages, carbon trading & many others, are ongoing & producing significant academic outputs & commercial benefits. We collaborate with numerous Government Public Sector, Defence and Industries in Australia and internationally. Our most recent key industry and government funded projects include:
In the modern world, e-commerce interactions are increasingly being carried out in virtual environments, thereby increasing the possibility of fraudulent transactions due to non-compliance by either communicating party. As such, there is an increased need for developing tools which help in making informed interaction-based decisions. Risk-based Decision Support System (RDSS) is a complete and comprehensive methodology developed at DEBII for assessing, expressing and managing risk in e-commerce interactions. RDSS is the first and only one of its type for risk assessment, measurement and management in e-commerce interactions. The objective of the project is to assess, analyse the level of risk as a function of its constituents in collaborative environments, and then manage it while decision-making. In order to achieve this, RDSS develops an architectural framework to ascertain and model the level of performance risk and financial risk according to the specific characteristics of the interaction, and according to their uncertainty when determining each of them at a certain point in time in the future. The risk in the interaction is then analysed and quantified according to its constituents by using two mathematical measures; the possibility theory and fuzzy logic. The output is then presented to the user in graphical format for better understanding. Based on the analysed risk, RDSS then carries out the steps of risk management and utilises it while making informed interaction-based decisions. For risk management, RDSS utilises a mathematical approach which determines the impact of the interaction initiating the agent’s risk propensity on the determined level of risk in an interaction, based on which it recommends an interaction-based decision. It provides the user with an effective decision-making methodology in an open interaction environment. The output of the project, when applied to interactions in virtual environments, would help the interacting agent to maximise its interaction experience and expected benefits.
Business interactions are the engine which drives the economy of the modern world. By business interactions, we mean the multi-disciplinary areas in that domain and which might have financial implications to either agent involved. The interactions in these domains are carried out with the aim of achieving certain specific outcomes which are consequential for the progression, advancement and sustenance for the particular business or individual. Failure to achieve those specific outcomes might have far reaching consequences to the business or individual. One of the important outcomes of the result of failure might be the risk of experiencing financial loss in such interactions. 18 Centre of Excellence for Logistics Innovation and Information Dominance Research 2019 – 2020 Centre of Excellence for Logistics Innovation and Information Dominance Research 2019 – 2020 19 In this project, we analyse and assess this risk as an important constituent of making informed decisions within a broader perspective of business interactions. One of the areas in that domain in this project for risk quantification is the probabilistic assessment of loss in revenue generation in Demand-Driven Production. In today’s competitive world, manufacturers are constantly subjected to massive pressure to reduce their operational costs and at the same time improve or increase their production efficiency. Cost reduction relating to production is not a bad thing for the manufacturers, but doing this implies that they have to shift or to adopt a new process for producing or manufacturing their goods. One such process that the manufacturers have to adopt is to produce and deliver the consumers’ orders within a fixed timeframe in order to obtain the required revenue from the transactions. In this project, we consider processes from the manufacturers’ perspective and assess the probabilistic level of risk incurred by not fulfilling the required demand within the given period. We also look at the level of financial consequences to the manufacturer as a result of not fulfilling the required demand. The output of this project will have far-reaching consequences when applied to the manufacturing industry.
The transportation system contributes 18% of the nation’s carbon emissions. Diesel powered logistics vehicle are a major contributor to this. Conversion of these diesel trucks to LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) will help achieve better economies and emissions profiles. This poses challenges and requires strong evidence to convince truck companies of the benefits. This is achieved by real time monitoring of the Diesel to LNG converted trucks in actual operation and different contexts. This information is then aggregated in a repository using a web enabled Cyber Physical System. This is analysed using knowledge discovery techniques. This knowledge is used to develop and design an intelligent controller for the LNG/Diesel converted trucks.
The emergence of data with complex structures is evident in many domains such as, Bioinformatics, Chemistry, Web Intelligence applications, Business Process Modelling, scientific knowledge management, etc. When such data sources are used, the attributes of the domain are often organised in a hierarchical (tree) or graph structure to enable a more semantic representation of (complex) properties and relationships of data objects. Mining of such data poses additional challenges in the data mining field, as it requires the development of data mining methods capable of taking into account the complex structures of the data and preserving the relationships and structural properties in the extracted knowledge patterns. To enable association rule mining of tree-structured data (e.g. XML), we have developed a general framework for mining of frequent ordered and unordered induced / embedded subtrees from a database of rooted, ordered, labelled trees using any of the existing support definitions. A number of important applications of tree mining are also investigated, such as web mining, knowledge matching, protein structure analysis and mining of health information. More recent work is focused on the use of classification and clustering techniques on tree-structured data.
Traditional research on data quality and data cleaning focuses on individual records (i.e. intra-record) stored on the databases. A number of techniques have been proposed for data cleansing using common statistical, clustering or inference based techniques. All of these operate on the schema level and intra-instance levels only to clean existing data in the database. They do not provide any method to ensure that future data entered into the system is free from errors. Our focus in on a data cleansing approach that operates on the business logic, schema, record matching and intra-instance levels so as to not only clean existing data errors in a given database, but ensures that newly entered data are error free. Automated and scalable data mining techniques are used in each of the phases of data cleansing process, to identify common and unexpected types of errors in the database. Automated techniques are used to detect the source of the data quality problems through business activity and system logic monitoring, and prevent their re-occurrence by validation and standardisation of both data entry and business executions.
Digital information within an enterprise consists of (1) structured data and (2) semi-structured/unstructured content. The structured data includes enterprise and business data like sales, customer and product information, accounts, inventory, etc. while the content includes contracts, emails, customer opinions, transcribed calls, etc. The structured data is managed by the relational database system (RDB), the semi/ unstructured content is managed by the content manager, and these two exist as silos. This leads to information of different types being in their own silos being managed and queried separately. This is undesirable since the information content of these sources is complementary. This project is concerned with developing a methodology and techniques for deriving business intelligence and novel knowledge from structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information conjointly. This methodology would be useful in several business intelligence and information integration applications, such as managing customer attrition, targeted marketing, fraud detection and prevention, compliance and customer relationship management as well as a number of fields which involve information of high complexity such as Bioinformatics, Logistics, Business and Electrical Power Systems (EPS). The broad aims of the project are to:
- use structured data to disambiguate text segments and link them to records for BI investigations
- use ontologies to disambiguate and annotate content segments to permit BI investigations
- develop methods of BI analysis for conjoint analysis of linked structured and content elements
- Apply these techniques for investigation of business problems, biomedical problems and EPS.
This project develops methodologies and systems to allow logistic companies to form coalitions with worldwide logistic providers. Using this approach, supply chain services and physical resources are coupled and extended beyond their typical region of operation. It involves the coupling of e-Transportation, e-Warehousing, e-Hub Connector and one-stop-shop, P2P (Partner to Partner) and B2B (Business to Business). This has the potential of allowing medium sized, regionally based, logistics providers to compete on the world stage with giant logistic providers such as UPS and FedEx. The project builds up a virtual collaborative logistics consortium that is especially suited to SME (small medium enterprise) supply chain providers, partners and alliances. The proposed IT infrastructure will allow the seamless exchange of information between the international logistics partners wherever they are and whenever it is necessary. This enables global supply chain management for all national / international clients, partners, customers, suppliers and buyers around the world to track the details and movement of goods anywhere at any time. The system also supports the need for communication and co-ordination between all partner transporters and warehouses around the world.
Global warming is becoming a big problem and carbon emissions from a variety of sources are the cause of it. To control emission, a number of carbon emission reduction policies and schemes such as the Kyoto Protocol & COP15 treaty have been reached and put in place. Many accounting models have already been proposed 20 Centre of Excellence for Logistics Innovation and Information Dominance Research 2019 – 2020 Centre of Excellence for Logistics Innovation and Information Dominance Research 2019 – 2020 21 in the current literature to solve the problem of responsibility ambiguity. However, the current accountability models are proposed for the general industries and not for the aviation industry. We feel that these models cannot be applied directly to the aviation industry since factors of influence are significantly different. In Aviation, it involves a mix of international and national factors such as the accountability and the implications of members and non-members of the climate change treaties in different countries. Hence, taking into account all the determinant factors and different stakeholders involved in the process of the carbon accounting, we are proposing an efficacious and fair accountability model for the aviation industry in our research. This accountability model can be used to assist Australian government in coming up with a fair tax ‘relief/ subsidy’ scheme for the aviation companies for more sustainable tourism to the country; since inclusion of aviation into the carbon reduction scheme is going to be taxing to the aviation and tourism industry growth.
The aim of this research is to propose and validate a framework for carrying out defeasible argumentative reasoning in semantic web applications. Web is a source of huge amount of data and semantic web efforts are targeted towards making web data contents machines understandable. This will have significant impact on the way information is exchanged and businesses are conducted. As ontology layer of semantic web has got enough maturity (i.e. standards like RDF, RDFs, OWL, OWL 2) the next step is to work on logic layer for development of advance reasoning capabilities for knowledge extraction and efficient decision making. Adding logic to web means use of rules to make inferences. Rules are a way to express business processes, policies, contracts etc but most of the studies have focused on use of monotonic logics in layered development of semantic web which provides no mechanism for representing mechanism for representing incomplete information and handling of contradictory information. These limitations are inherited in Description Logics being subset of predicate logic. Defeasible logic programming is based on nonmonotonic logic and has been used in software agents for carrying out goal driven defeasible reasoning. Defeasible reasoning is a rule based approach to perform reasoning on incomplete, inconsistent and uncertain information and priorities are used to resolve conflicts among rules. Semantic web is source of defeasible knowledge as its open by nature and subject to inconsistencies deriving from multiple sources; therefore, it is not possible to define priorities in advance among conflicting rules. Additionally, quantitative approaches for reasoning on semantic web are also criticized for their in ability to generate easy to understand and logically clear result. We are interested in to exploiting the power of defeasible logic and argumentation for data driven reasoning on semantic web by identifying the issues involved in mapping of RDF/OWL ontologies to defeasible logic programming, how to carry out argumentative reasoning on semantic web, how DeLP rules can be shared on web and how tractable, customizable results can be represented to user.
This research aims to develop a framework to particularly assist Software Engineering Ontology evolution and management by using a semantic wiki based approach. Software Engineering Ontology encompasses common shareable software engineering knowledge and software engineering concepts, how and why they are related. However, most existing ontologies including the Software Engineering Ontology are derived from a single perspective which can be complicated for users, have a lack of maintainability, and become obsolete and impracticable ontologies. Additionally, the knowledge encoded in the ontologies is not static but should evolve. To overcome these impediments to the Ontology Evolution, this research will use a semantic wiki based approach which provides an environment for discussion and formalizing ontology issues, supports ontology evolution, and assist maintaining the versions of ontology. Ontology evolution is one of the main issues that Ontology users face today. The issues include lack of communication between offshore and onshore staff in the development and evolving ontology in Defence domain. Additionally, a lot of work for ontology engineers involves updating the ontology manually. The process of evolving the ontology requires work from the domain experts. There has not been a cost effective communication method to discuss and agree upon the changes. In this project, the use of a lightweight community-driven approach is developed in order to enhance the communication on the ontology evolution. This will enable a more efficient and effective method to communicate and take decisions in a better way.
